Porting a Python Webscraper to AWS Lambda
I have a webscraper that I’ve written with beautifulsoup4 to scrape indeed for a list of skills associated with GIS and how many jobs are associated with those skills. The results are returned as a JSON list.
Now this is very useful by itself, but what if I want to have it be a serverless function that can be run from anywhere and not have to run it on my local machine? Maybe I could even have it run at set intervals and store the results in a database later.
Well luckily there’s something called AWS lambda that lets me do just that. Here’s how to port your python functions to lambda.
Let’s take a look at this code.
#This will be a lambda function
#@Author: Benjamin Johnson
import json
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
import time
def lambda_handler(event, context):
#'C%23'='C#', #'C+2B%2B'='C++',
#Key: used in the page url for scraping, Value: human readable version written to output
terms={"GIS":"GIS","GIS+Python":"GIS Python","GIS+Java":"GIS Java", "GIS+SQL":"GIS SQL",
"GIS+Ruby":"GIS Ruby", "GIS+Javascript":"GIS Javascript","GIS+HTML":"GIS HTML",
"GIS+CSS":"GIS CSS", "GIS+C":"GIS C", "GIS+C%23":"GIS C#", "GIS+C%2B%2B":"GIS C++",
"GIS+BASH":"GIS Bash", "GIS+SHELL":"GIS Shell", "GIS+UNIX":"GIS Unix",
"GIS+PHP":"GIS PHP", "GIS+typescript":"GIS Typescript","GIS+SWIFT":"GIS Swift",
"GIS+OBJECTIVE+C":"GIS Objective C", "GIS+.NET":"GIS .Net", "GIS+MATLAB":"GIS MATLAB",
"GIS+MAPBOX":"GIS MapBox", "GIS+ARCGIS":"GIS ArcGIS","GIS+Rust":"GIS Rust",
"GIS+QGIS":"GIS QGIS", "GIS+LEAFLET":"GIS Leaflet", "GIS+PostgreSQL":"GIS PostgreSQL",
"GIS+SQL+SERVER":"GIS SQL Server", "GIS+ORACLE":"GIS Oracle", "GIS+NOSQL":"GIS NoSQL",
"GIS+MONGODB":"GIS MongoDB", "GIS+Cassandra":"GIS Cassandra","GIS+REDIS":"GIS Redis",
"GIS+HBASE":"GIS HBASE", "GIS+DYNAMODB":"GIS DynamoDB", "GIS+AWS":"GIS AWS",
"GIS+HADOOP":"GIS HADOOP", "GIS+AutoCAD":"GIS AutoCAD","GIS+CIVIL3D":"GIS Civil3D",
"GIS+VBA":"GIS VBA", "GIS+ERDAS+IMAGINE":"GIS ERDAS IMAGINE", "GIS+ENVI":"GIS ENVI",
"GIS+GDAL":"GIS GDAL", "GIS+CAD":"GIS CAD"}
jobs=[]
for key, value in terms.items():
page = requests.get("https://www.indeed.com/jobs?q="+key)
soup = BeautifulSoup(page.content, 'html.parser')
n_jobs = 0
#if no results returned from the page then .group(0) will kick up an error
try:
for meta in soup.find_all('meta', attrs={"name": "description"}):
n_jobs = re.search('\d+', meta["content"].replace(',','')).group(0)
except:
print("no results for {value}".format(value=value))
scrape_info={
'input' : event,
'status_code' : page.status_code,
'search term' : value,
'number of jobs' : n_jobs,
'date' : time.strftime("%d_%m_%Y")
}
print(scrape_info)
jobs.append(scrape_info)
return jobs
Notice that I’ve called my function lambda_handler, this is important for portability with lambda. The python file must also be called lambda_function.py
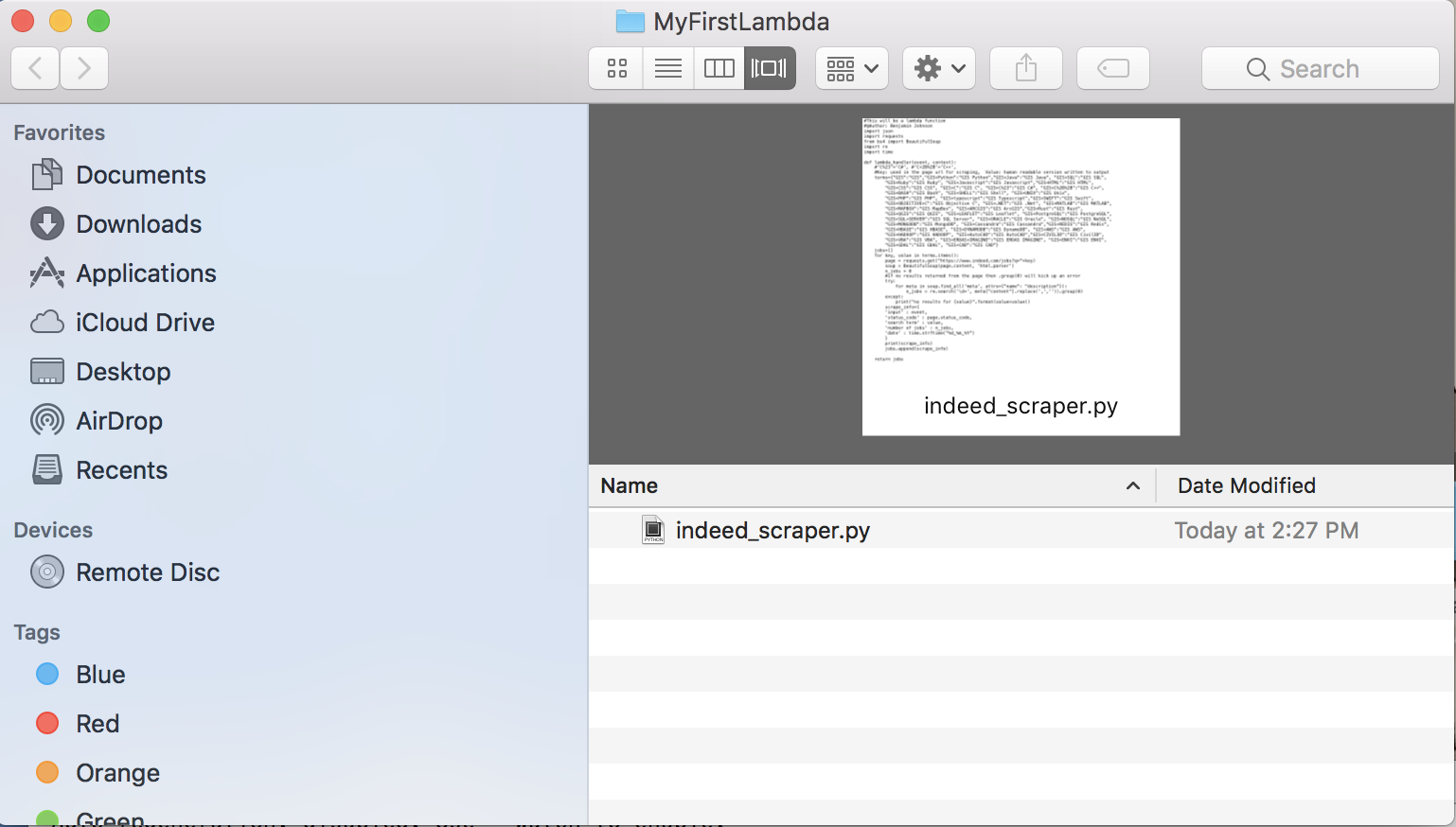
This is the folder that I have my function in. I have it named indeed_scraper.py so I will need to rename it to lambda_function.py.
My function relies on packages that are not included in the standard library, namely beautifulsoup4 and requests. We will need to install these packages locally.
We can do this by adding the -t flag to pip.
pip3 install requests -t /Users/benjohnson/desktop/MyFirstLambda/
pip3 install bs4 -t /Users/benjohnson/desktop/MyFirstLambda/If the packages were successfully installed, your folder should look like this:
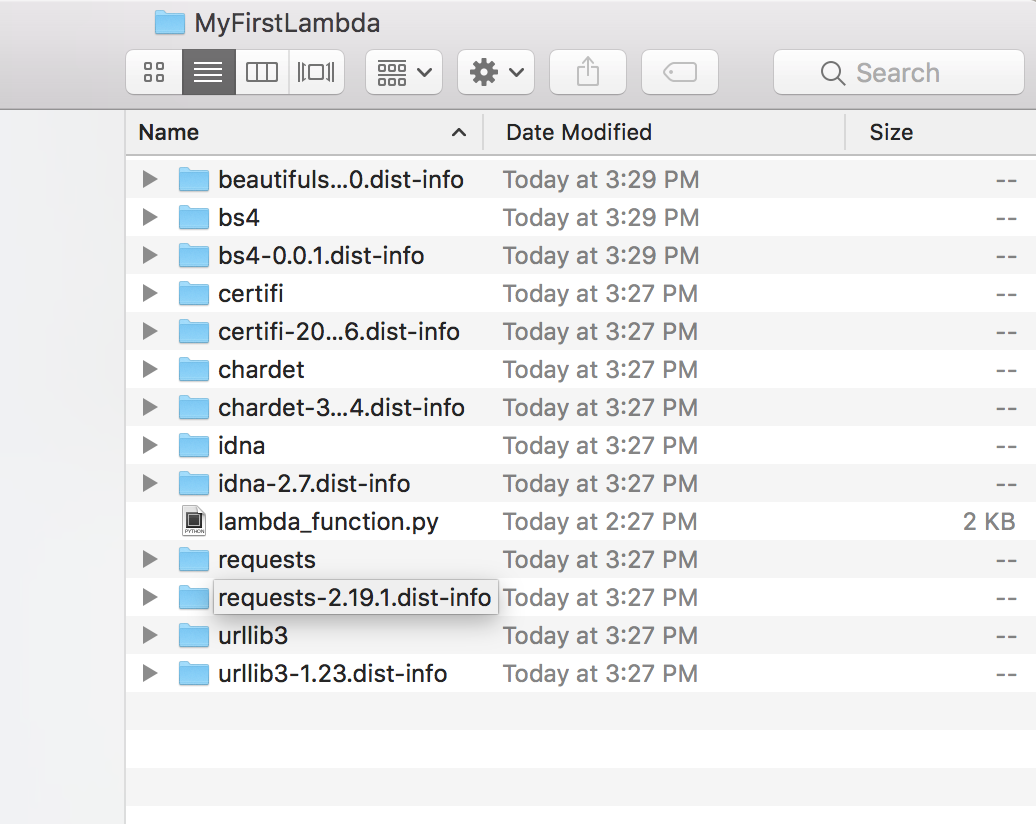
Change directory into this folder and create a .zip
cd desktop
cd MyFirstLambda
zip -r MyFirstLambda.zip ./Follow the steps outlined in an earlier tutorial to create a basic lambda function
Go to your lambda page and upload the .zip with your python file and package contents.
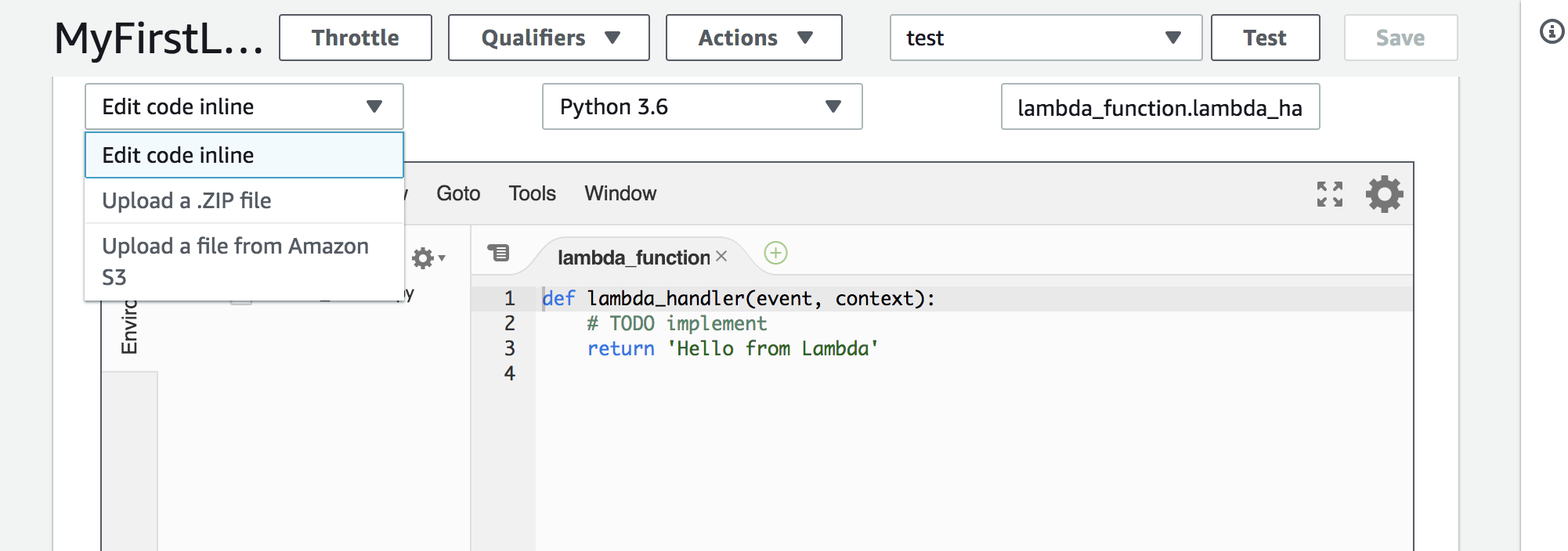
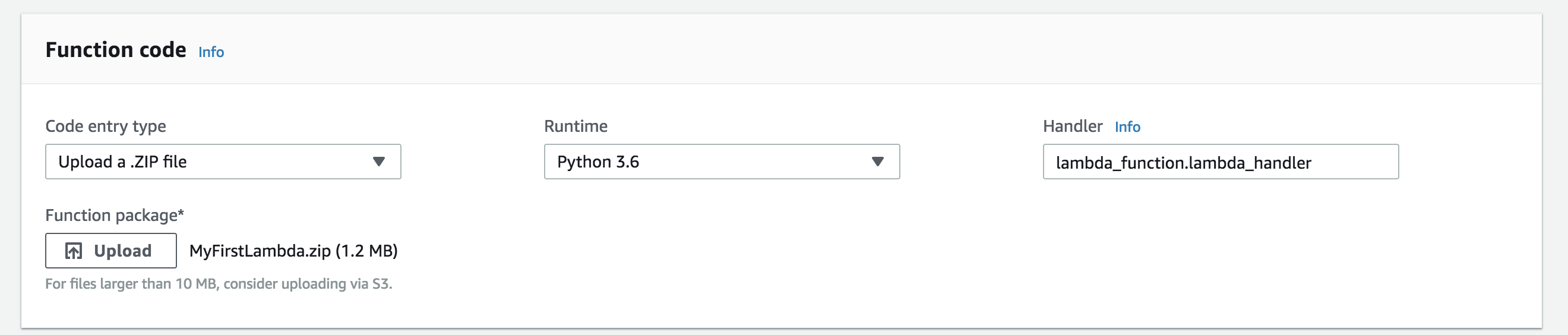
Hit save to upload your files. If it worked your code should appear in the code window.
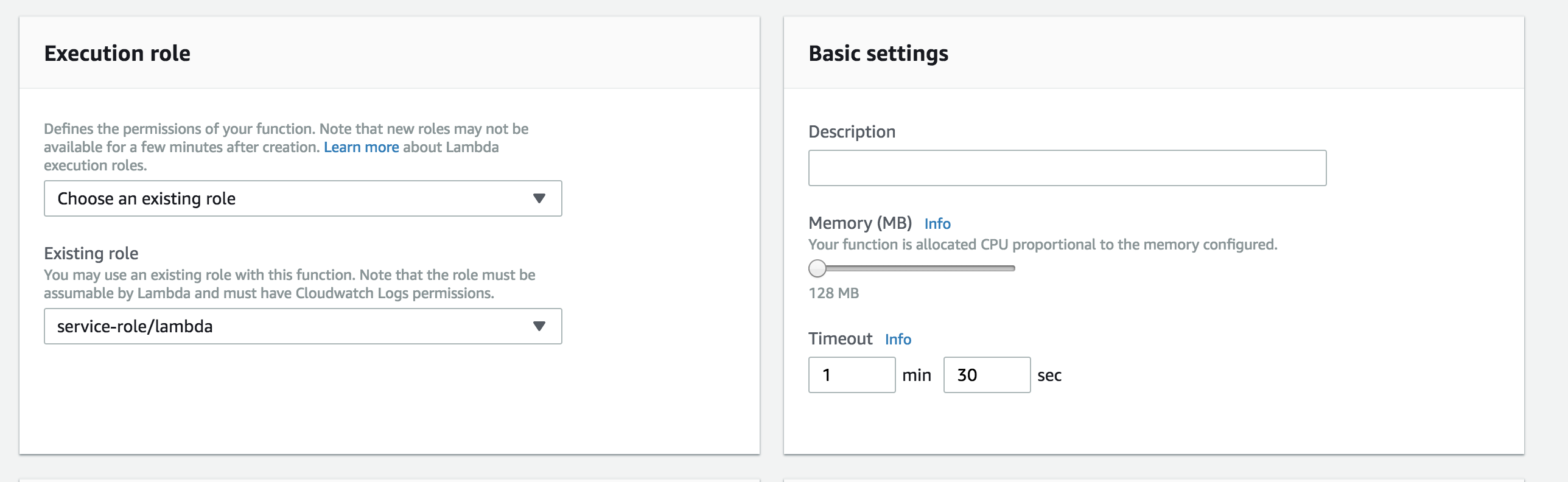
My function takes about 60 seconds to run, so I will increase the max allowed runtime from 3 seconds to 1 min 30 seconds.
Save and hit the test button when you are ready, the test input doesn’t matter here because we are scraping from predefined website URLs and don’t use any input.
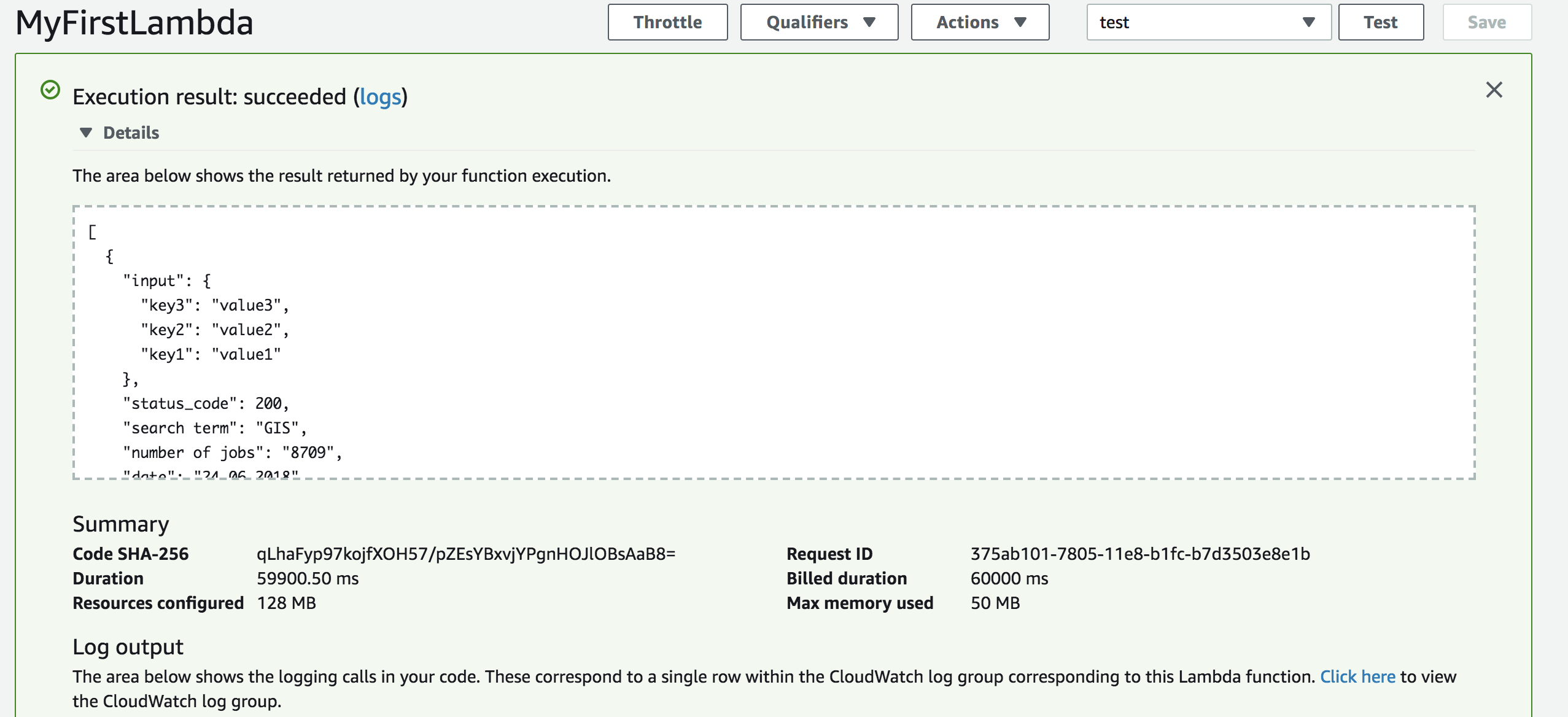
A successfull web scraping! The output is returned as a JSON list, and we can easily store it with whatever AWS service we choose. Since we are using python we would need to use the boto3 package on Amazon to achieve this.
